Creating a Bridge With a Dead Letter Sink (DLS)
What is a Dead Letter Sink?
A Dead Letter Sink is a construct that allows the user to configure a destination for events that would otherwise be dropped due to some delivery failure. This is useful for scenarios where you want to ensure that events are not lost due to a failure in the underlying system.
Example scenario
In this example we are going to use a WebhookSource object that will received HTTP calls and send events to the Broker named demo. An event viewer, named event-success-capture will subscribe to the Webhook events flowing through the Broker using a Trigger.
The Broker delivery options will be set to use a Dead Letter Sink so that in the case of a delivery error the event will be forwarded to another event viewer service named event-failure-capture instead of being lost into the void.
We will test to make sure events are delivered to event-success-capture, then we will break the bridge by removing the event-success-capture service, in which case we expect the Dead Letter Sink to receive all events that were not delivered.
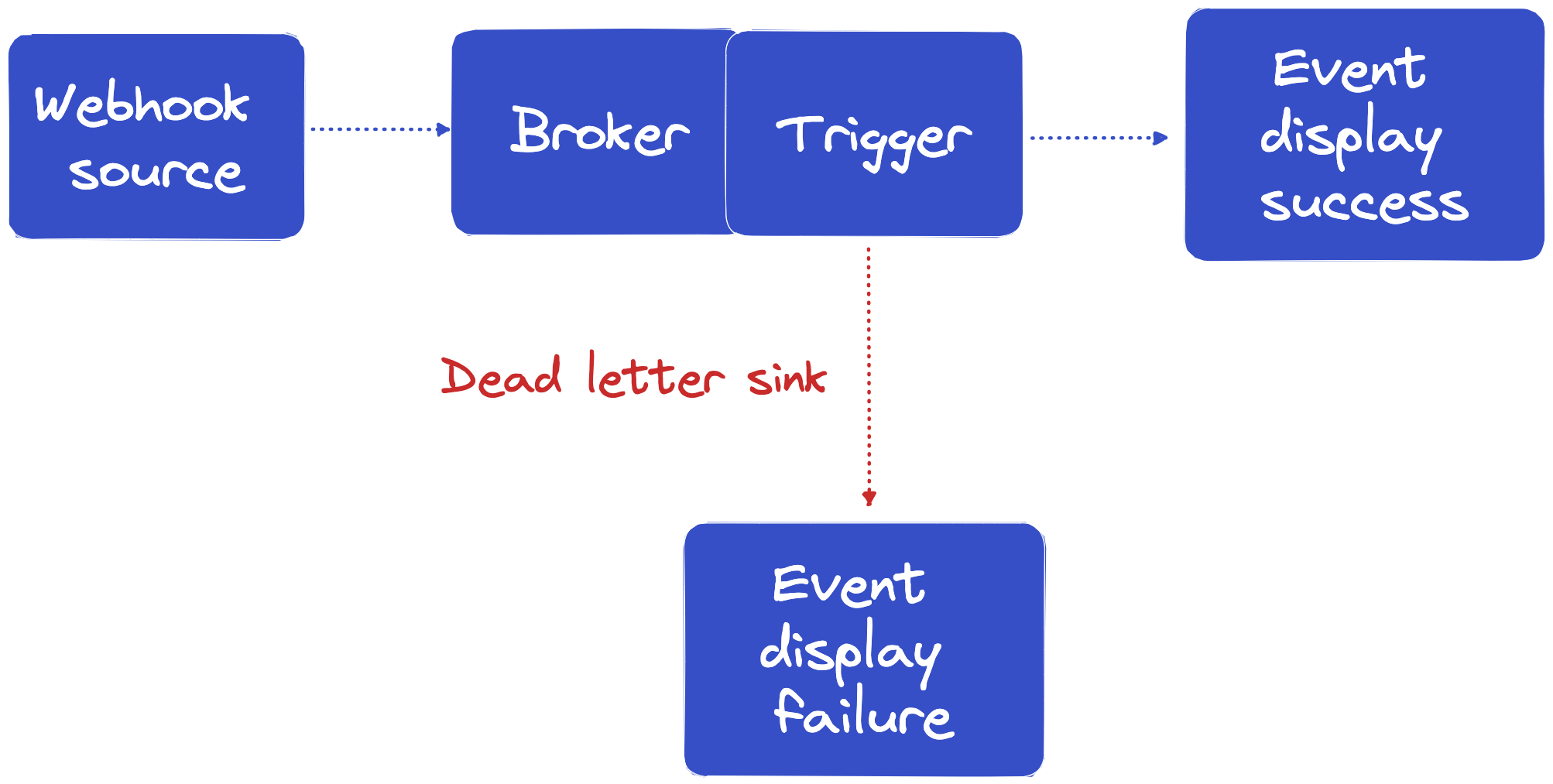
Setting up TriggerMesh with a Dead Letter Sink
Creating objects
All objects mentioned at this guide are intended to be created at kubernetes.
When using kubectl write the provided YAML manifests to a file and write at a console:
Alternatively if you don't want to write the manifests to a file you can use this command:
Kubernetes manifest
The next steps create the configuration that demonstrates the usage of the Dead Letter Sink. A single manifest containing all the objects can be downloaded here.
Step 1: Create the Broker
Create a new Broker with following configuration:
Step 2: Create the WebhookSource
Create a WebhookSource object with the following configuration:
apiVersion: sources.triggermesh.io/v1alpha1
kind: WebhookSource
metadata:
name: webhook
spec:
eventType: webhook.event
sink:
ref:
apiVersion: eventing.triggermesh.io/v1alpha1
kind: MemoryBroker
name: demo
This object will expose an HTTP endpoint to which you can send a payload that will be turned into a CloudEvent and sent to the Broker created in the previous step.
Step 3: Create the event-success-capture Service
Create a Service named event-success-capture with the following configuration:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: event-success-capture
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels: &labels
app: event-success-capture
template:
metadata:
labels: *labels
spec:
containers:
- name: event-display
image: gcr.io/knative-releases/knative.dev/eventing/cmd/event_display
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: event-success-capture
spec:
selector:
app: event-success-capture
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
That service will write to its standard output any CloudEvent received. We will use a Trigger to subscribe to all events flowing through the Broker.
Step 4: Create the demo-to-display Trigger
Create a Trigger to route events to the event-success-capture Service with the following configuration:
apiVersion: eventing.triggermesh.io/v1alpha1
kind: Trigger
metadata:
name: demo-to-display
spec:
broker:
group: eventing.triggermesh.io
kind: MemoryBroker
name: demo
target:
ref:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
name: event-success-capture
delivery:
deadLetterSink:
ref:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
name: event-failure-capture
backoffDelay: "PT0.5S" # ISO8601 duration
backoffPolicy: exponential # exponential or linear
retry: 2
Here a Trigger named demo-to-display is configured with the following properties
- configures the Broker to send all ingested events to the event-success-capture service.
In terms of delivery options:
- 2 retries on failure, backing off exponentialy with a 0.5 seconds factor. This is not the focus of this article but it is recommended to setup retries before giving up on delivery and sending to the DLS.
- Dead Letter Sink pointing to a service named
event-failure-capture.
Step 5: Create the event-failure-capture Service
Create the Service named event-failure-capture that was configured at the Broker as the Dead Letter Sink parameter:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: event-failure-capture
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels: &labels
app: event-failure-capture
template:
metadata:
labels: *labels
spec:
containers:
- name: event-display
image: gcr.io/knative-releases/knative.dev/eventing/cmd/event_display
---
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: event-failure-capture
spec:
selector:
app: event-failure-capture
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 8080
This service should only receive messages that could not be delivered to a destination.
Test the Bridge
Make sure that all created objects are ready by inspecting the READY column after this command:
$ kubectl get memorybrokers.eventing.triggermesh.io,triggers.eventing.triggermesh.io,service
NAME URL AGE READY REASON
memorybroker.eventing.triggermesh.io/demo http://demo-mb-broker.deadlettersink.svc.cluster.local 118s True
NAME BROKER TARGET_URI AGE READY REASON
trigger.eventing.triggermesh.io/demo-to-display demo http://event-success-capture.deadlettersink.svc.cluster.local 42s True
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/demo-mb-broker ClusterIP 10.101.11.31 <none> 80/TCP 114s
service/event-failure-capture ClusterIP 10.108.26.194 <none> 80/TCP 118s
service/event-success-capture ClusterIP 10.110.30.137 <none> 80/TCP 118s
service/webhooksource-webhook ExternalName <none> kourier-internal.knative-serving.svc.cluster.local 80/TCP 102s
service/webhooksource-webhook-00001 ClusterIP 10.102.145.249 <none> 80/TCP,443/TCP 108s
service/webhooksource-webhook-00001-private ClusterIP 10.110.149.207 <none> 80/TCP,443/TCP,9090/TCP,9091/TCP,8022/TCP,8012/TCP 108s
Retrieve the URL where the Webhook is listening for incoming requests.
$kubectl get webhooksources.sources.triggermesh.io webhook
NAME READY REASON URL SINK AGE
webhook True http://webhooksource-webhook.deadlettersink.127.0.0.1.sslip.io http://demo-mb-broker.deadlettersink.svc.cluster.local 4m14s
Use curl or any HTTP capable client to post an event to the webhook.
curl -d '{"message":"test my bridge"}' http://webhooksource-webhook.deadlettersink.127.0.0.1.sslip.io
The broker should then deliver the event to the event-success-capture, while event-failure-capture should not be receiving any event. We can confirm that by reading each of those services output:
$ kubectl logs deployments/event-success-capture
2023/03/08 18:10:27 Failed to read tracing config, using the no-op default: empty json tracing config
☁️ cloudevents.Event
Context Attributes,
specversion: 1.0
type: webhook.event
source: deadlettersink.webhook
id: a9097eb8-4cbe-436b-b226-d6b9d59013b6
time: 2023-03-08T18:16:20.535991218Z
datacontenttype: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Data,
{"message":"test my bridge"}
As expected the event-success-capture is receiving events produced by PingSource.
$ kubectl logs deployments/event-failure-capture
2023/03/08 18:10:28 Failed to read tracing config, using the no-op default: empty json tracing config
Meanwhile event-failure-capture is not showing any event.
Test Failing Bridge
To make the Bridge fail will be removing the event-success-capture service. That will make the delivery fail and (after 2 retries) be sent to the Dead Letter Queue.
$ kubectl delete svc event-success-capture
service.serving.knative.dev "event-success-capture" deleted
Send another event to the Webhook source:
curl -d '{"message":"test my bridge"}' http://webhooksource-webhook.deadlettersink.127.0.0.1.sslip.io
After doing so, all events not delivered by Broker through the configured Trigger will be shown at the event-failure-capture:
$ kubectl logs deployments/event-failure-capture
2023/03/08 18:10:28 Failed to read tracing config, using the no-op default: empty json tracing config
☁️ cloudevents.Event
Context Attributes,
specversion: 1.0
type: webhook.event
source: deadlettersink.webhook
id: f6e0fa6b-cde8-4a80-b9f5-2a199fff873c
time: 2023-03-08T18:21:10.993992297Z
datacontenttype: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Data,
{"message":"test my bridge"}
Clean up
Clean up the remaining resources by issuing this command:
kubectl delete svc event-failure-capture
kubectl delete deployments.apps event-failure-capture
kubectl delete deployments.apps event-success-capture
kubectl delete triggers.eventing.triggermesh.io demo-to-display
kubectl delete webhooksources.sources.triggermesh.io webhook
kubectl delete memorybrokers.eventing.triggermesh.io demo